Microsoft on Tuesday released 58 patches affecting 15 product families. Five of the addressed issues, all involving Azure, are considered by Microsoft to be of Critical severity, though only two require urgent attention (more on that below). Fifteen have a CVSS base score of 8.0 or higher, including two with a 9.8 base score. Six are known to be under active exploit in the wild, and three are publicly disclosed (including one not yet known to be under exploit).
At patch time, five CVEs are judged more likely to be exploited in the next 30 days by the company’s estimation, in addition to the six already detected to be so. Various of this month’s issues are amenable to direct detection by Sophos protections, and we include information on those in a table below. The release also includes advisory information on three Edge patches released last week.
We are as always including at the end of this post appendices listing all Microsoft’s patches sorted by severity (Appendix A), by predicted exploitability timeline and CVSS Base score (Appendix B), and by product family (Appendix C). Appendix E provides a breakout of the patches affecting the various Windows Server platforms.
By the numbers
- Total CVEs: 58
- Publicly disclosed: 3
- Exploit detected: 6
- Severity
- Critical: 5
- Important: 52
- Moderate: 1
- Impact:
- Denial of Service: 3
- Elevation of Privilege: 26
- Information Disclosure: 6
- Remote Code Execution: 11
- Security Feature Bypass: 5
- Spoofing: 7
- CVSS base score 9.0 or greater: 2
- CVSS base score 8.0 or greater: 15
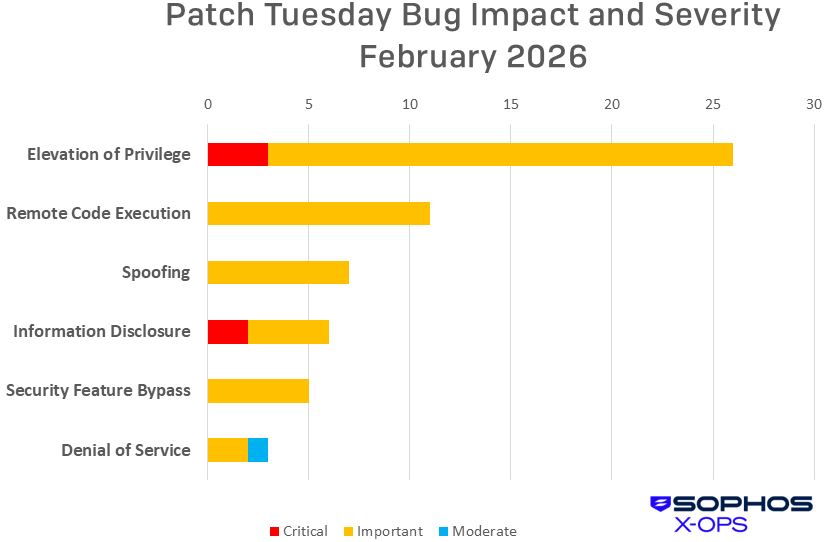
Figure 1: Elevation of Privilege issues were once again the most common type in February’s patches
Products
- Windows: 31
- Azure: 10
- 365: 6
- Office: 6
- Visual Studio: 4
- Excel: 3
- SharePoint: 2
- Word: 2
- .NET: 1
- Defender for Linux: 1
- Exchange: 1
- JetBrains: 1
- Notepad: 1
- Power BI: 1
- Windows App for Mac: 1
As is our custom for this list, CVEs that apply to more than one product family are counted once for each family they affect. We note, by the way, that CVE names don’t always reflect affected product families closely. In particular, some CVEs names in the Office family may mention products that don’t appear in the list of products affected by the CVE, and vice versa.
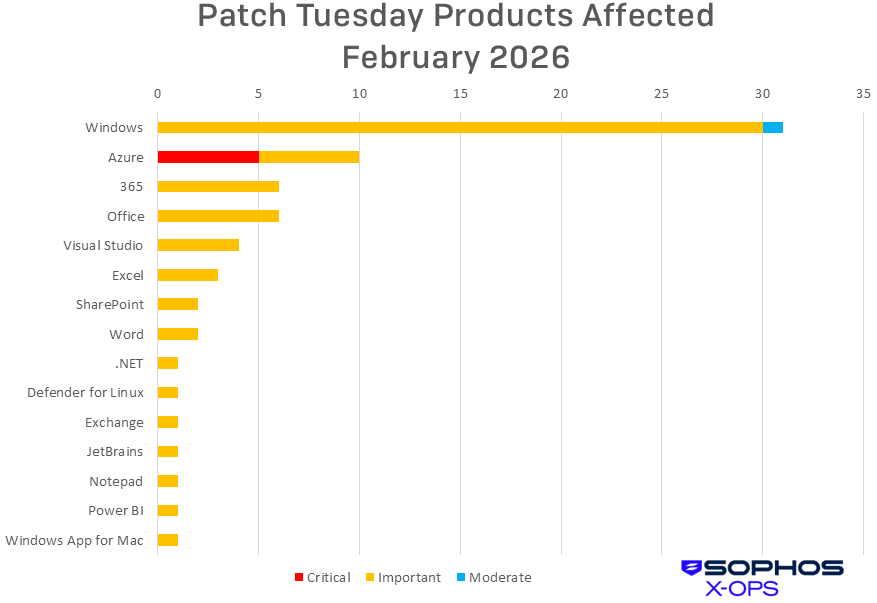
Figure 2: Windows had (as it usually does) the biggest patch set this month, but Azure owned all the Critical-severity CVEs. Three of those Critical-severity issues were patched ahead of Patch Tuesday, but two affecting ACI Confidential Containers were not
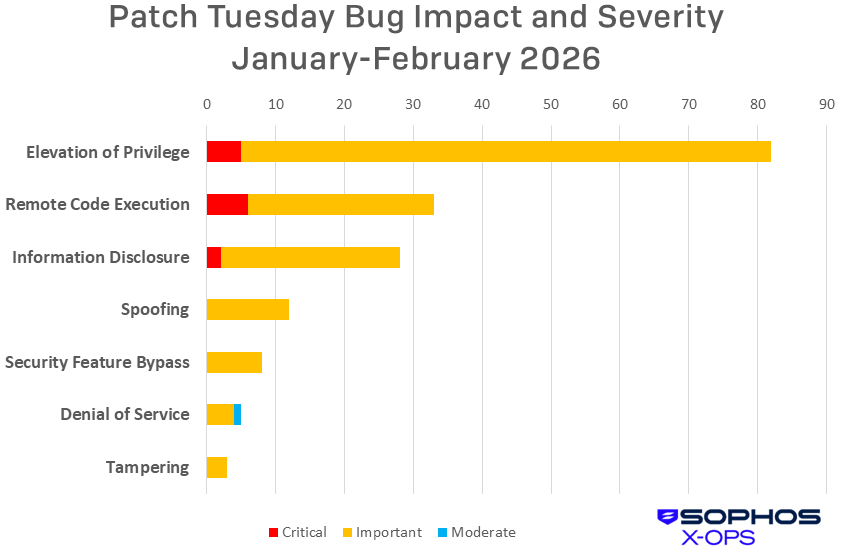
Figure 3: It seems that 2026 is The Year Of Unfortunately Elevated Privilege… at least so far
Notable February updates
In addition to the issues discussed above, several specific items merit attention.
CVE-2026-21510 -- Windows Shell Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
One of the three February vulnerabilities that has been publicly disclosed and is currently under active attack in the wild, this CVE is a nasty little piece of work – according to Microsoft, “an attacker could bypass Windows SmartScreen and Windows Shell security prompts by exploiting improper handling in Windows Shell components, allowing attacker‑controlled content to execute without user warning or consent.” It also affects all supported versions of Windows (both client and server), making this CVE an easy choice to prioritize this month.
CVE-2026-21513 -- Internet Explorer Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
CVE-2026-21514 -- Microsoft Word Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability
Both of these security feature bypass vulnerabilities are under active exploit in the wild; the Word CVE, which Microsoft lists as affecting 365 and Office but no specific version of Word, is one of the three that has been publicly disclosed this month. The two patches also share sequential CVE numbers (occasionally a sign that they were discovered in the course of a single investigation), a reliance on OLE, and an easy path to exploitation – all the target needs to do is click a malicious link or, for Office, open a malicious document.
CVE-2026-21260 -- Microsoft Outlook Spoofing Vulnerability
CVE-2026-21511 -- Microsoft Outlook Spoofing Vulnerability
Identically named but differing substantially in expected exploitability, both of these CVEs affect 365, Office, SharePoint, and Word (Outlook, though mentioned in the title, does not figure in the affected-products list published by Microsoft) and both can be triggered via Preview Pane. CVE-2026-21511 has been publicly disclosed and Microsoft considers it more likely to be exploited within the next 30 days. Near-term exploitation of CVE-2026-21260, on the other hand, is thought to be unlikely.
CVE-2026-21531 -- Azure SDK for Python Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
It’s good that this CVSS Base 9.8 bug is likely hard to exploit, because based on the description it just might manage to be both RCE and EoP in nature. According to Microsoft’s information, “an attacker could supply a maliciously crafted continuation token that, when processed by the Azure AI Language Conversations Authoring SDK, triggers unsafe deserialization and executes attacker‑controlled code on the system using the SDK.” Bad vibes only.
Sophos protections
| CVE | Sophos Intercept X/Endpoint IPS | Sophos XGS Firewall |
|---|---|---|
| CVE-2026-21231 | Exp/2621231-A | Exp/2621231-A |
| CVE-2026-21238 | Exp/2621238-A | Exp/2621238-A |
| CVE-2026-21241 | Exp/2621241-A | Exp/2621241-A |
| CVE-2026-21253 | Exp/2621253-A | Exp/2621253-A |
| CVE-2026-21510 | sid:2312232 | sid:2312232 |
| CVE-2026-21513 | sid:2312235 | sid:2312235 |
| CVE-2026-21514 | Exp/2621514-A, sid:2312237, sid:2312238 | sid:2312233 |
| CVE-2026-21519 | Exp/2621519-A | Exp/2621519-A |
| CVE-2026-21525 | Exp/2621525-A | Exp/2621525-A |
| CVE-2026-21533 | Exp/2621533-A | Exp/2621533-A |
As you can every month, if you don’t want to wait for your system to pull down Microsoft’s updates itself, you can download them manually from the Windows Update Catalog website. Run the winver.exe tool to determine which build of Windows you’re running, then download the Cumulative Update package for your specific system’s architecture and build number.
Appendix A: Vulnerability Impact and Severity
This is a list of February patches sorted by impact, then sub-sorted by severity. Each list is further arranged by CVE.
Elevation of Privilege (26 CVEs)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2026-21522 | Microsoft ACI Confidential Containers Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-24300 | Azure Front Door Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-24302 | Azure Arc Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21229 | Power BI Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21231 | Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21232 | Windows HTTP.sys Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21234 | Windows Connected Devices Platform Service Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21235 | Windows Graphics Component Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21236 | Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21237 | Windows Subsystem for Linux Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21238 | Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21239 | Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21240 | Windows HTTP.sys Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21241 | Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21242 | Windows Subsystem for Linux Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21245 | Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21246 | Windows Graphics Component Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21250 | Windows HTTP.sys Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21251 | Cluster Client Failover (CCF) Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21253 | Mailslot File System Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21257 | GitHub Copilot and Visual Studio Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21259 | Microsoft Excel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21508 | Windows Storage Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21517 | Windows App for Mac Installer Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21519 | Desktop Windows Manager Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21533 | Windows Remote Desktop Services Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
Remote Code Execution (11 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-2804 | Red Hat, Inc. CVE-2023-2804: Heap Based Overflow libjpeg-turbo |
| CVE-2026-20841 | Windows Notepad App Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21228 | Azure Local Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21244 | Windows Hyper-V Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21247 | Windows Hyper-V Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21248 | Windows Hyper-V Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21256 | GitHub Copilot and Visual Studio Code Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21516 | GitHub Copilot for Jetbrains Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21523 | GitHub Copilot and Visual Studio Code Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21531 | Azure SDK for Python Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21537 | Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Linux Extension Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Spoofing (7 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21218 | .NET and Visual Studio Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21249 | Windows NTLM Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21260 | Microsoft Outlook Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21511 | Microsoft Outlook Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21512 | Azure DevOps Server Cross-Site Scripting Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21527 | Microsoft Exchange Server Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21529 | Azure HDInsight Spoofing Vulnerability |
Information Disclosure (6 CVEs)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2026-21532 | Azure Function Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-23655 | Microsoft ACI Confidential Containers Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21222 | Windows Kernel Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21258 | Microsoft Excel Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21261 | Microsoft Excel Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21528 | Azure IoT Explorer Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
Security Feature Bypass (5 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21255 | Windows Hyper-V Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21510 | Windows Shell Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21513 | Internet Explorer Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21514 | Microsoft Word Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21518 | GitHub Copilot and Visual Studio Code Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
Denial of Service (3 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-20846 | GDI+ Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21243 | Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| Moderate severity | |
| CVE-2026-21525 | Windows Remote Access Connection Manager Denial of Service Vulnerability |
Appendix B: Exploitability and CVSS
This is a list of the five February CVEs judged by Microsoft to be more likely to be exploited in the wild within the first 30 days post-release, along with the six CVEs already known to be under attack. The list is arranged by CVE.
| Exploitation detected | |
| CVE-2026-21510 | Windows Shell Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21513 | Internet Explorer Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21514 | Microsoft Word Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21519 | Desktop Windows Manager Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21525 | Windows Remote Access Connection Manager Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21533 | Windows Remote Desktop Services Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Exploitation more likely within the next 30 days | |
| CVE-2026-21231 | Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21238 | Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21241 | Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21253 | Mailslot File System Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21511 | Microsoft Outlook Spoofing Vulnerability |
These are the February CVEs with a Microsoft-assessed CVSS Base score of 8.0 or higher. They are arranged by score and further sorted by CVE. For more information on how CVSS works, please see our series on patch prioritization schema.
| CVSS Base | CVSS Temporal | CVE | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9.8 | 8.5 | CVE-2026-21531 | Azure SDK for Python Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| 9.8 | 8.5 | CVE-2026-24300 | Azure Front Door Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2026-20841 | Windows Notepad App Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2026-21255 | Windows Hyper-V Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2026-21256 | GitHub Copilot and Visual Studio Code Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| 8.8 | 8.2 | CVE-2026-21510 | Windows Shell Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2026-21513 | Internet Explorer Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2026-21516 | GitHub Copilot for Jetbrains Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| 8.8 | 7.7 | CVE-2026-21537 | Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Linux Extension Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| 8.6 | 7.5 | CVE-2026-24302 | Azure Arc Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| 8.2 | 7.1 | CVE-2026-21532 | Azure Function Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| 8.1 | 7.1 | CVE-2026-21228 | Azure Local Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| 8.0 | 7.0 | CVE-2026-21229 | Power BI Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| 8.0 | 7.0 | CVE-2026-21257 | GitHub Copilot and Visual Studio Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| 8.0 | 7.0 | CVE-2026-21523 | GitHub Copilot and Visual Studio Code Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Appendix C: Products Affected
This is a list of February’s patches sorted by product family, then sub-sorted by severity. Each list is further arranged by CVE. Patches that are shared among multiple product families are listed multiple times, once for each product family. Certain issues for which advisories have been issued are covered in Appendix D, and issues affecting Windows Server are further sorted in Appendix E. All CVE titles are accurate as made available by Microsoft; for further information on why certain products may appear in titles and not product families (or vice versa), please consult Microsoft.
Windows (31 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2023-2804 | Red Hat, Inc. CVE-2023-2804: Heap Based Overflow libjpeg-turbo |
| CVE-2026-20846 | GDI+ Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21222 | Windows Kernel Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21231 | Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21232 | Windows HTTP.sys Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21234 | Windows Connected Devices Platform Service Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21235 | Windows Graphics Component Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21236 | Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21237 | Windows Subsystem for Linux Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21238 | Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21239 | Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21240 | Windows HTTP.sys Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21241 | Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21242 | Windows Subsystem for Linux Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21243 | Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Denial of Service Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21244 | Windows Hyper-V Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21245 | Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21246 | Windows Graphics Component Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21247 | Windows Hyper-V Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21248 | Windows Hyper-V Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21249 | Windows NTLM Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21250 | Windows HTTP.sys Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21251 | Cluster Client Failover (CCF) Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21253 | Mailslot File System Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21255 | Windows Hyper-V Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21508 | Windows Storage Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21510 | Windows Shell Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21513 | Internet Explorer Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21519 | Desktop Windows Manager Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21533 | Windows Remote Desktop Services Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Moderate severity | |
| CVE-2026-21525 | Windows Remote Access Connection Manager Denial of Service Vulnerability |
Azure (10 CVEs)
| Critical severity | |
| CVE-2026-21522 | Microsoft ACI Confidential Containers Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21532 | Azure Function Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-23655 | Microsoft ACI Confidential Containers Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-24300 | Azure Front Door Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-24302 | Azure Arc Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21228 | Azure Local Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21512 | Azure DevOps Server Cross-Site Scripting Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21528 | Azure IoT Explorer Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21529 | Azure HDInsight Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21531 | Azure SDK for Python Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
365 (6 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21258 | Microsoft Excel Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21259 | Microsoft Excel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21260 | Microsoft Outlook Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21261 | Microsoft Excel Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21511 | Microsoft Outlook Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21514 | Microsoft Word Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
Office (6 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21258 | Microsoft Excel Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21259 | Microsoft Excel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21260 | Microsoft Outlook Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21261 | Microsoft Excel Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21511 | Microsoft Outlook Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21514 | Microsoft Word Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
Visual Studio (4 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21256 | GitHub Copilot and Visual Studio Code Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21257 | GitHub Copilot and Visual Studio Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21518 | GitHub Copilot and Visual Studio Code Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21523 | GitHub Copilot and Visual Studio Code Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Excel (3 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21258 | Microsoft Excel Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21259 | Microsoft Excel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21261 | Microsoft Excel Information Disclosure Vulnerability |
SharePoint (2 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21260 | Microsoft Outlook Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21511 | Microsoft Outlook Spoofing Vulnerability |
Word (2 CVEs)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21260 | Microsoft Outlook Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-21511 | Microsoft Outlook Spoofing Vulnerability |
.NET (1 CVE)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21218 | .NET and Visual Studio Spoofing Vulnerability |
Defender for Linux (1 CVE)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21537 | Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Linux Extension Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Exchange (1 CVE)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21527 | Microsoft Exchange Server Spoofing Vulnerability |
JetBrains (1 CVE)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21516 | GitHub Copilot for Jetbrains Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Notepad (1 CVE)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-20841 | Windows Notepad App Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Power BI (1 CVE)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21229 | Power BI Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
Windows App for Mac (1 CVE)
| Important severity | |
| CVE-2026-21517 | Windows App for Mac Installer Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability |
Appendix D: Advisories and Other Products
There are three Edge-related advisories listed in February’s release:
| CVE-2026-0391 | Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based) for Android Spoofing Vulnerability |
| CVE-2026-1861 | Chromium: CVE-2026-1861 Heap buffer overflow in libvpx |
| CVE-2026-1862 | Chromium: CVE-2026-1862 Type Confusion in V8 |
Appendix E: Affected Windows Server versions
This is a table of the 31 CVEs in the February release affecting Windows Server versions 2012 through 2025. The table differentiates among major versions of the platform but doesn’t go into deeper detail (eg., Server Core). An “x” indicates that the CVE does not apply to that version. The Windows App for Mac patch (CVE-2026-21517, Windows App for Mac Installer Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability) does not appear in this table.
Administrators are encouraged to use this appendix as a starting point to ascertain their specific exposure, as each reader’s situation, especially as it concerns products out of mainstream support, will vary. For specific Knowledge Base numbers, please consult Microsoft.
| CVE | S-12 | 12r2 | S-16 | S-19 | S-22 | 23h2 | S-25 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2023-2804 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | × |
| CVE-2026-20846 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21222 | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | × | × |
| CVE-2026-21231 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21232 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21234 | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21235 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | × | × |
| CVE-2026-21236 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21237 | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21238 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21239 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21240 | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21241 | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21242 | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21243 | × | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21244 | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21245 | × | × | × | × | × | × | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21246 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21247 | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21248 | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21249 | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21250 | × | × | × | × | × | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21251 | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21253 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21255 | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21508 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21510 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21513 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21519 | × | × | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21525 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
| CVE-2026-21533 | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ | ■ |
.svg?width=185&quality=80&format=auto&cache=true&immutable=true&cache-control=max-age%3D31536000)


.svg?width=13&quality=80&format=auto&cache=true&immutable=true&cache-control=max-age%3D31536000)


